What is Agribusiness? An Overview of the Agricultural Industry
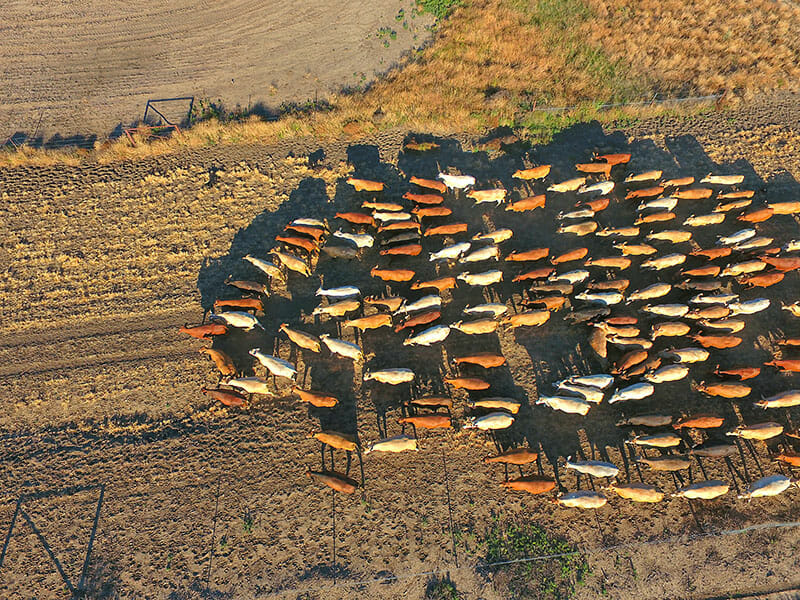
Agribusiness is a term that combines agriculture and business, referring to any commercial activity related to farming and food production, through all stages of the process starting at pre-farm all the way through to retail.
The agribusiness industry is an essential part of the global economy, contributing significantly to the GDP of many countries. In highly industrialised countries, many activities essential to agriculture are carried out separately from the farm. Agribusiness has become increasingly important in recent years due to the growing demand for food and the need to feed a growing global population.
The industry faces many challenges, including climate change, water scarcity, and the need to produce more food with fewer resources. As the world’s population continues to grow, the agribusiness industry will play a critical role in ensuring that there is enough food to feed everyone. In Australia particularly, farming and agribusiness play a significant role in our regional and rural areas, not only having a consequential impact on local economies, but also on the social wellbeing with many agribusinesses embedded and connected within their communities and families.
Definition of Agribusiness
Agribusiness is a term used to describe all the activities involved in producing and distributing agricultural products. It encompasses all aspects of agriculture, from crop production and farming operations to the sale of agricultural commodities, including companies that produce fertilisers and pesticides, farming equipment manufacturers, food distribution companies, and more.
The agribusiness sector includes a wide range of enterprises involved in producing, processing, and distribution of food and fibre products and by-products, as well as cultivated products for consumer use. It is a complex industry that requires a wide range of skills, including farming, marketing, finance, and agribusiness management.
This industry is an essential part of the economy, as it provides food and other agricultural products to consumers throughout Australia and worldwide.
History of the Agribusiness Industry
The history of agribusiness can be traced back to the early days of agriculture, when farmers began to specialise in certain crops and began to trade their surplus with other farmers. As agriculture became more sophisticated, so did the businesses that supported it.
The modern agribusiness industry began to take shape in the early 20th century, as advances in technology and transportation made it possible to produce and distribute agricultural products on a large scale. The introduction of new farming techniques, such as mechanisation and the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, also helped to increase agricultural productivity and efficiency.
Today, agribusiness is a major industry that plays a critical role in feeding the world’s growing population. As the demand for food and other agricultural products continues to increase, agribusiness will remain an important and dynamic industry that is constantly evolving to meet the needs of consumers and farmers alike.
Types of Agricultural Production in Agribusiness
Agribusiness is a broad term that encompasses all commercial activities related to farming, agriculture and retail food supply. It includes a wide range of industries, from farming and ranching to forestry and fishing. Here are some of the main types of agribusiness:
Farming
Farming is the cultivation of crops and the rearing of livestock for food, fuel, and other products. This includes everything from small-scale family farms to large commercial operations. Farming can be divided into several categories, including:
- Arable farming: the cultivation of crops like wheat, corn, and barley
- Livestock farming: the rearing of animals like cows, pigs, and chickens for meat, milk, and eggs
- Mixed farming: a combination of arable and livestock farming
Grazier
Graziers rear livestock on a large scale, typically in a semi-arid or arid environment. Graziers produce animals like cattle, sheep, and goats for meat, wool, and milk. Graziers often manage a lot of land, and have to deal with issues like drought, wildfires, and predators.
Forestry
Forestry is the management of forests for timber, paper, and other wood products. Foresters plant and harvest trees, manage forest ecosystems, and protect forests from pests, diseases, and wildfires. Forestry also involves the conservation of wildlife habitats and the preservation of biodiversity.
Fishing
Fishing is the harvesting of fish and other aquatic animals for food, sport, and other purposes. Fishermen use a variety of techniques, from nets and traps to lines and hooks, to catch fish in freshwater and saltwater environments. Fishing can be a sustainable industry when managed properly, but overfishing and other environmental issues can threaten fish populations.
Role of Agribusiness in the Economy
Agribusiness plays a vital role in the economy of many countries. The sector provides employment opportunities to a significant percentage of the population, especially in rural areas. In addition, it contributes to the overall economic growth of a country through exports and the supply of raw materials to other industries.
The following are some of the ways in which agribusiness contributes to the economy:
Employment
Agribusiness provides employment opportunities to millions of people worldwide. According to the World Bank, the sector employs approximately 26% of the global population, the majority of which is in developing nations. In developing countries, agriculture accounts for up to 70% of total employment. The sector provides jobs not only in farming but also in processing, packaging, transportation, and marketing of agricultural products.
Finance & Income Generation
Agribusiness generates income for farmers and other stakeholders in the supply chain. By providing a market for their products, farmers can earn a decent income and improve their standard of living. In addition, agribusiness creates opportunities for entrepreneurs to invest in processing, packaging, and marketing of agricultural products, which generates income for themselves and their employees.
Exports
Agribusiness is a significant contributor to the export earnings of many countries. Agricultural products such as coffee, tea, cocoa, and fruits are some of the most traded commodities in the world. In addition, agribusiness provides a market for other industries such as manufacturing, which rely on agricultural raw materials.
Food Security
Agribusiness plays a critical role in ensuring food security in many countries. By producing enough food to meet the needs of the population, agribusiness reduces the reliance on food imports, which can be expensive and unreliable. In addition, agribusiness promotes the adoption of modern farming techniques and technologies, which increase productivity and reduce post-harvest losses.
Challenges Facing Agribusiness
Agribusiness faces many challenges that can threaten the industry’s sustainability and profitability. In this section, we will discuss three major challenges facing agribusiness today: climate change, market volatility, and supply chain issues.
Climate Change
Climate change is a significant challenge facing the agribusiness industry. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are impacting crop yields, soil health, and water availability. As a result, farmers are facing increased costs, reduced yields, and greater risks.
Adapting to climate change requires significant investment in research and development, new technologies, and infrastructure. For example, farmers may need to invest in irrigation systems, drought-resistant crops, and precision agriculture technologies to manage water and nutrient use more efficiently.
Market Volatility
Market volatility is a significant challenge for agribusiness. Prices for agricultural commodities can be volatile, driven by factors such as weather, supply and demand, and geopolitical events. This volatility can make it difficult for farmers to plan and manage their businesses effectively.
To manage market volatility, farmers and agribusinesses must develop strategies to hedge against price fluctuations, such as forward contracts, futures, and options. Additionally, they may need to diversify their operations to reduce their exposure to any one commodity.
Supply Chain Issues
Supply chain issues are another significant challenge facing agribusiness. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains, with disruptions to transportation, labour, and processing facilities impacting the availability of agricultural products.
To mitigate supply chain risks, agribusinesses must develop resilient and flexible supply chains. This may involve investing in local processing facilities, diversifying suppliers, and building strategic partnerships with other stakeholders in the supply chain.
Opportunities in Agribusiness
Agribusiness is a rapidly growing sector that presents numerous opportunities for investors, entrepreneurs, and farmers. The industry is constantly evolving, and new technologies and practices are emerging to improve productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. This section will explore some of the opportunities in agribusiness, including technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Technological Advancements
One of the most significant opportunities in agribusiness is the adoption of new technologies. From precision agriculture to biotechnology, there are numerous ways that technology can improve productivity and efficiency in the sector. For example, precision agriculture uses GPS, sensors, and other technologies to monitor crops and soil conditions, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions about planting, fertilising, and harvesting. Biotechnology, on the other hand, involves the use of genetic engineering to create crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, or that have higher yields.
Other technological advancements in agribusiness include:
- Robotics and automation: Robots can be used for tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting, reducing the need for manual labour and increasing efficiency.
- Drones: Drones can be used to monitor crops, assess soil conditions, and spray pesticides and fertilisers.
- Big data: The use of big data analytics can help farmers make more informed decisions about planting, fertilising, and harvesting, based on data such as weather patterns and market demand.
Sustainable Practices
Another significant opportunity in agribusiness is the adoption of sustainable practices. With increasing concerns about climate change and environmental degradation, there is growing demand for food that is produced in an environmentally friendly way. Sustainable practices can also improve efficiency and reduce costs, making them an attractive option for farmers and agribusinesses.
Some examples of sustainable practices in agribusiness include:
- Organic farming: Organic farming involves the use of natural fertilisers and pest control methods, and avoids the use of synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms.
- Conservation agriculture: Conservation agriculture involves practices such as reduced tillage, cover cropping, and crop rotation, which help to improve soil health and reduce erosion.
- Agroforestry: Agroforestry involves the integration of trees into farming systems, providing benefits such as shade, windbreaks, and improved soil fertility.
Agribusiness presents numerous opportunities for investors, entrepreneurs, and farmers. Technological advancements and sustainable practices are just two examples of the ways that the industry is evolving to meet the challenges of the future. By embracing these opportunities, agribusinesses can improve productivity, efficiency, and sustainability, while also meeting the growing demand for food that is produced in an environmentally friendly way.
Future of Agribusiness
The future of agribusiness looks promising, with the industry poised to undergo significant changes in the coming years. Advancements in technology and shifting consumer demands are driving this transformation. Here are some of the key trends that are shaping the future of agribusiness:
AgTech
AgTech, or agricultural technology, is one of the most significant trends in agribusiness. The sector is expected to triple in size, with the market worth $12.4 billion in 2020 and projected to reach $34.1 billion by 2026. In Australia alone, there are over 300-400 young startup companies that are seeking game-changing digital technologies to enhance their operations. These technologies include precision agriculture, drones, robotics, and artificial intelligence, among others. They help farmers to reduce costs, increase yields, and improve efficiency.
Sustainability
Sustainability is another critical trend that is shaping the future of agribusiness. Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of food production. As a result, there is a growing demand for sustainably produced food. This trend is driving the adoption of sustainable farming practices, such as regenerative agriculture, organic farming, and vertical farming. These practices help to reduce the environmental impact of food production while also improving the quality of the food.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences are changing, and this is having a significant impact on the future of agribusiness. Consumers are looking for healthier, more sustainable, and more ethically produced food. This trend is driving the adoption of plant-based diets, which are becoming increasingly popular. As a result, there is a growing demand for alternative protein sources, such as plant-based meat substitutes.
Globalisation
Globalisation is also shaping the future of agribusiness. The industry is becoming increasingly global, with more and more food being produced and consumed across borders. This trend is driving the need for improved supply chain management, logistics, and food safety standards. It is also creating new opportunities for farmers and agribusinesses to expand their operations and tap into new markets.
The Business of Agriculture is More Accessible Than Ever with the Right Financing
The global role agribusiness has to play is critical for a sustainable future. At SproutAg, we know a big part of ensuring the effectiveness of agricultural production and processes is simplified and stress-free access to financing when you need it most.
Our specialised team are experienced in agribusiness finance, business advisory, succession planning and all things finance in farming. Contact our team today to learn how we can help secure the financing your agribusiness needs.